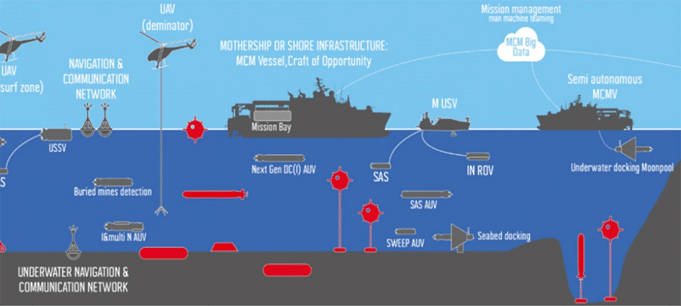
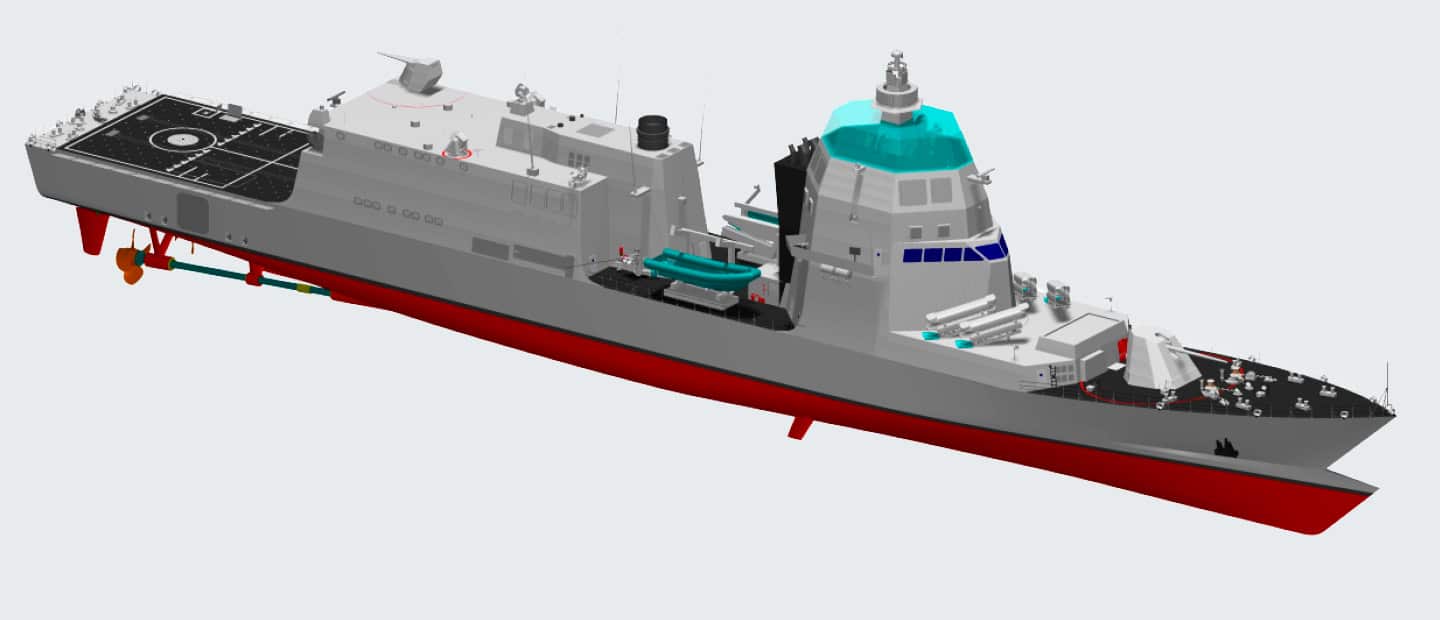
Shipping traffic is recognised as the main man-noise source of the anthropogenic noise generated in the marine environment. The underwater acoustic pollution is increased due to the increment of the human activity at seas supposing a threat for marine habitats. The ship as acoustic source must be understood and controlled to manage the maritime areas both in time and space to reduce the impact of noise in marine fauna.
Shipping noise is mainly composed of flow noise, propeller noise and machinery noise. This research is focused on the analysis and estimation of the underwater radiated noise generated by the vibrations of the onboard machinery or structure-borne noise based on the calculation of the transfer function. This function relates the acceleration levels of the vibrations of the hull’s panels and the radiated noise by them using the radiation efficiency. Different analytical methods to estimate the radiation efficiency are presented and compared with data collected at sea.
The measurements are performed acquiring simultaneously acceleration and acoustic levels by means on accelerometers installed on the hull’s panels at different positions and hydrophones deployed close to the bow, middle and stern of the ship. The analysis of the transmission of the vibrations along the ships is performed using the data from different locations of the hydrophones. The quality of the measurements is analysed using the coherence function through the spectral correlation between the measurement of vibrations and acoustic levels.
On the other hand, signal-to-noise ratio is computed to verify the strength of the noise sources. The computed transfer function is used to predict the underwater radiated noise from vibrations showing differences less than 2 dB re to 1 uPa2.
Read the full paper here: